How Are Solar Panels Made?
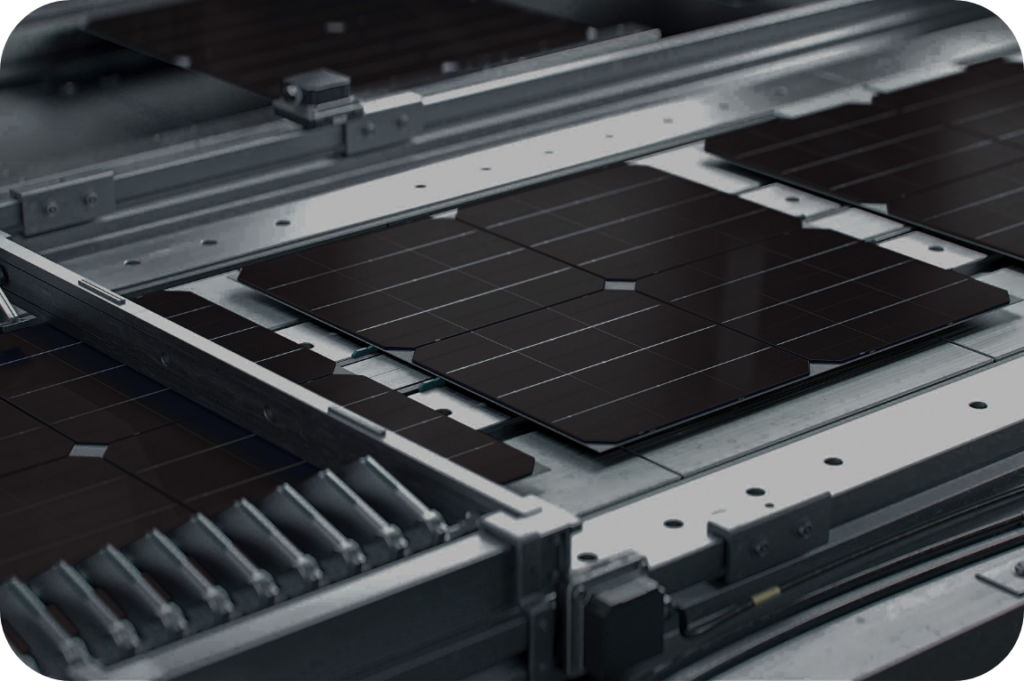

When you think about it, solar panels are pretty amazing. They turn sunlight into usable energy that can power your entire household — and the most amazing part is they’re actually a fairly simple technology when you break down the manufacturing process! The core components of a solar panel really only include silicon, solar cells, glass, and metal.
This is a topic that we at Axia by Qcells know a thing or two about. Qcells is the manufacturer of the most widely used solar panels in residential and commercial installations across the country. Plus, our panels are assembled right here in the United States at our Dalton, Georgia factory.
If you’ve ever wondered how solar panels are made or what solar panels are made of, we’re here to explain the process step by step.
What Are Solar Panels Made of?
It all starts with silicon.
Silicon is derived from everyday beach sand, the raw material used to make solar panels. It is far and away the most common material used to make photovoltaic (PV) cells, comprising around 95% of all modules sold. The United States obtains most of its silicon from the South and Midwest.
Silicon crystals are made up of interconnected silicon atoms in a crystal lattice. It’s this lattice structure that is so conducive to efficiently converting light into electricity.


Did you know?

Step 1: Purify Silicon and Add Boron
The first step of the manufacturing process is to collect and purify silicon. Converting raw materials into high-quality silicon is an energy-intensive process that is done by melting quartz sand in an electric furnace at extremely high temperatures to form cylinder-shaped ingots. The melting process must be done with great care to ensure the alignment of the atoms in the proper orientation. Once the ingot is cool, it will be polished until it has flat sides.
During the melting process, the silicon is treated with boron to create a positive electrical charge.

Step 2: Cut Ingots into Wafers
Next, the ingots are precisely cut into wafers as thin as paper using a wire saw. These wafers require an anti-reflective coating to prevent the reflection of sunlight, which reduces the panel’s ability to absorb sunlight and generate energy.
Step 3: Treat the Wafers
The wafers from Step 3 are then treated with a sunlight-absorbing coating and given metal conductors to produce a grid-like surface that can convert sunlight into electricity. Then, to create a negative electrical charge, a thin layer of phosphorus is applied on top of the wafers in a hot chamber. Now having a positive-negative junction, the cell is capable of generating electricity.

Step 4: Configure the Solar Cells
Finally, solder any metal connectors to link the cells together in a matrix-like configuration. Solar panels typically have between 48 and 72 cells, depending on the size of the application and the energy needs.

Step 5: Frame the Cells
Once the cells are connected, they are sealed into a vinyl or rubber acetate. The panel is placed in a frame under a sheet of 6-7 mm glass on the front side and polymer-based material on the backside to keep dirt, water, and other foreign substances from getting in.

Step 6: Test the Panel
The finished product is now ready to test for functionality and performance at fixed laboratory conditions, also called Standard Test Conditions (STC), which are consistent across the industry and allow for comparison against other products. Within the manufacturer’s facility, the panel is put in a flash tester, which reveals the voltage, efficiency, impact, temperature tolerance, solar power output, and current of the panel.
The panel is also carefully inspected and cleaned before being shipped to a business or a house.
What Are the Different Types of Solar Panels?
The three most common solar panel types include thin film, monocrystalline, and polycrystalline. These three types are structurally distinct and are each manufactured a little differently.
Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Monocrystalline solar panels are very similar to polycrystalline panels, but they have some differences. The primary distinction between them is that monocrystalline panels are obtained by manufacturing a single silicon crystal. It is more efficient in solar energy conversion, which increases the cost of monocrystalline solar panels.
Polycrystalline Solar Panels
When multiple silicon fragments are melted together, you get polycrystalline panels. Despite monocrystalline being more efficient, polycrystalline solar panels can still meet your home energy needs.
Thin-Film Solar Panels
Thin-film solar panels are a low-efficiency variety, so you’d need many panels to generate sufficient power. Rather than being composed of solar cells, they’re made by adding a thin layer of photovoltaic material on a glass surface. This makes them cost-effective, but they’re not usually used in homes because of their low efficiency and durability. These panel types are most often used for solar industry utility-scale projects.
Who Manufactures and Tests Solar Panels?
A lot of the solar manufacturing process is conducted with the help of robotics, which helps to lower the overall cost of solar panels for consumers. But while much of it is automated, some of it still has to be done by human beings. As of 2021, the solar industry employs over 255,000 American workers, according to the Solar Jobs Census!
Axia Solar is proudly powered by Qcells, a leading North American solar manufacturer known for performance and efficiency throughout the solar industry. Using Q.ANTUM Technology, Qcells is setting the standard for solar through a four-level quality program that ensures extended reliability and long-term profitability for the owner.

The Testing Process for New Solar Panels
With reputable solar companies, panels go through a rigorous quality assurance process so they can last their full lifetime. Throughout the manufacturing process, each part and material used is checked first for potential defects. If a solar cell is bent or cracked, it won’t be used in the final product. Once the panel is completed, the manufacturer will not only test the electrical current, but they’ll also make sure it can withstand extreme weather, falling debris, and everyday wear and tear.
Is it Possible to Make Your Own Solar Panels?
After reading this article, you might have wondered whether it’s possible to make a solar panel yourself if you have the materials. We recommend obtaining solar equipment from a professional solar company, so you know your panel will operate at maximum efficiency. Not only that — creating a panel can be hazardous without the proper training and experience. One wrong move and you could accidentally start a fire; the risks are simply not worth compromising your safety.
The Future of Solar is Bright
Solar manufacturing continues to become more efficient, enabling the industry to produce better solar panels each passing year. As the efficiency of the manufacturing process increases, the cost decreases, which makes energy independence possible for a wider variety of budgets.
If you’re interested in upgrading your home energy system to solar, now knowing how solar panels are made, Axia is ready to help you electrify your life! We make the solar process as seamless as possible, and we’re capable of designing an individually tailored solar system that works for your needs. Get in touch with us today to get a custom, no-obligation quote on high-quality solar products.