How Do Solar Panels Work?


Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels turn sunlight into energy that we can use to power homes and businesses — but how exactly does that process work? Generating energy from sunlight requires some complex science. If you’ve ever wondered how solar panels form one of the most sustainable energy sources ever discovered, we break down this technical process in a simple way below.
Here, you’ll learn how solar panels work and what they do, so you can understand the process from start to finish.
The Basics of Solar Energy: How Do Solar Panels Work?
Sunlight, also called solar radiation or electromagnetic radiation, emanates from the sun at varying levels worldwide. Solar panels can harness that electromagnetic radiation and turn it into usable energy. Read on to learn about the basics of solar energy and how solar panels work.

access varies based on location and time of year.

Solar PV modules, or solar panels, generate energy using sunlight. But solar panels are just one aspect of solar power systems, which need other technologies to work as intended. These technologies include mounting structures, building-integrated PV (BIPV), inverters, and storage. For solar panels to generate energy most efficiently, their location must be carefully calculated and secured by mounting structures. The mounting design should be sturdy and weatherproof. It should also position the panels to receive as much sunlight as possible based on factors like latitude, structural orientation, and electricity usage.
As solar panels produce direct current (DC) energy, inverters convert it into alternating current (AC) energy. An entire solar energy system typically uses just one inverter to convert direct current electricity into the electricity that powers our televisions, computers, appliances, and more.
Solar batteries are used for energy storage and help you get the most out of your solar power system. Excess energy produced on sunny days is stored in these batteries and can either be used on a day-to-day basis when the system is producing less power than you’re using or can remain on standby to provide backup power during a grid outage. Storage batteries are also used in net metering, where solar power system users can feed excess energy back to the grid and save on utility bills.

Solar Radiation and System Production
Depending on where you live, you may receive more or less solar radiation on any given day or any time of year. The amount of solar radiation you receive also fluctuates based on the location, landscape, season, and time of day. As we live on a round planet, the sun’s rays hit Earth at different angles. Areas closer to the earth’s equator will receive higher levels of sunlight consistently throughout the year, whereas locations nearer to the earth’s north and south poles will receive less. Sunlight levels also change during seasons. All of these factors influence how much energy solar panels produce at a given time.
Seasonality
In the summer, the United States is closer to the sun. So, the days are longer, and solar panels receive more light, allowing them to work more effectively. In the winter, when the U.S. is farther from the sun, solar panels still receive sunlight but at lower levels. Solar panels receive the most sunlight when the sun is at the highest point in the sky.
Weather
Just as solar radiation varies by the season, it can also vary day to day based on the weather. As you might expect, solar radiation is more limited on a cloudy day when compared with a sunny day. That doesn’t mean that solar panel production stops on a cloud day though. Panels can still produce at about 25% of their max on a cloudy day.
Roof Orientation
Roof orientation is also a determining factor in how effectively your panels capture sunlight and convert it to usable electricity. The direction of your roof is directly related to the amount of solar radiation your panels get. Ideally, your panels should face south in the Northern Hemisphere and north in the Southern Hemisphere for maximum exposure and optimal energy production.


Photovoltaics
What do solar panels do? As mentioned above, photovoltaic (PV) technology enables solar panels to transform sunlight into usable energy. PV cells, also called solar cells, are small devices made up of semiconductor materials. Each cell usually produces 1 or 2 watts1 and is surrounded by plastic, glass, or other materials that protect the technology from the elements.
Because each PV cell produces a relatively small amount of power, solar energy systems are made up of multiple PV cells strung together to form solar modules, also called solar panels. One solar panel can contain over a hundred cells depending on size and use, though specific numbers will vary by manufacturer. This makes solar energy systems modular and customizable based on need.
PV solar panels are manufactured all around the world and domestic production of solar equipment has increased significantly over the past several years. Qcells is one of the companies that is championing the creation of a domestic solar supply chain in order to make solar more affordable for homeowners across the country.
When Do Solar Panels Stop Working?
Since PV solar panels rely on solar radiation, it is normal for there to be periods of time when the solar system is inactive and not producing electricity. The most common situation is at night. When the sun goes down, solar panels stop producing electricity and the system automatically shuts down until the next morning when it turns back on with the return of sunlight.
Snow coverage also has the potential to keep solar panels from producing power. However, if some solar panels remain uncovered, they may produce power and help melt the snow on the rest of the system as they warm up.
Over time, solar panel systems tend to degrade in their production efficiency but it may take several decades before they stop working altogether. Top solar panel manufacturers like Qcells issue panel warranty for up to 20-30 years.
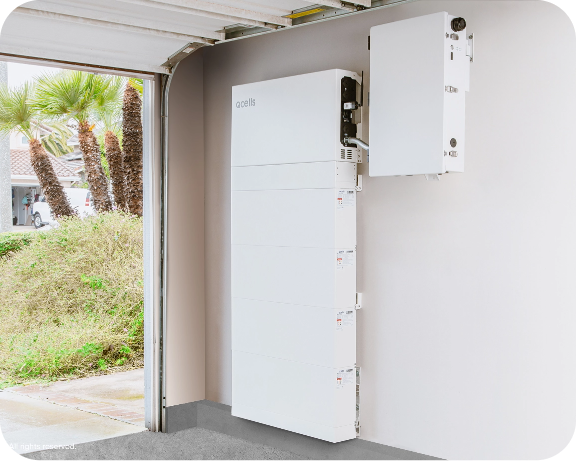


Storing Solar Power
Even though there are periods of time when solar panels are not producing power for use in the home, by attaching a solar battery to the system it is possible to power your home on solar even when the panels aren’t producing power.
Solar batteries store electricity produced by the solar system for use at night or when there’s a power outage. Depending on where you live, you may opt to install a solar battery to maximize solar savings, for emergency power during an outage or both!
Concentrating Solar-Thermal Power: A PV Alternative
Large power plants or utility-scale solar power systems generate more energy using concentrating solar-thermal power (CSP) technology. CSP can generate more electricity by using mirrors to reflect sunlight back into solar power receivers, concentrating the amount of solar radiation and maximizing energy generation.
CSP technology systems can be designed into thermal storage, power tower, and linear systems.

Thermal Storage Systems
Solar energy production can be limited when the sun sets or weather conditions are cloudy. Thermal storage systems offer a solution to this issue by reflecting sunlight onto receivers, generating heat, and producing electricity that can be used instantly or stored for later. Typical thermal storage systems include two-tank direct, two-tank indirect, and single-tank thermocline systems.
CSP Power Tower Systems
Concentrating solar-thermal power tower systems are made up of many sun-tracking mirrors called heliostats. The heliostats concentrate sun rays onto a solar receiver at the top of the tower. The receiver contains a heat-transfer fluid, which, when warmed, heats a working fluid used in a turbine generator to create electricity.
CSP Linear Systems
Concentrating solar-thermal linear systems work similarly to power towers. The main difference is that the sun-tracking mirrors, or heliostats, concentrate sunlight onto linear receiver tubes instead of a receiver on a tall tower.

CSP systems provide efficient and reliable renewable energy and play a vital role in overcoming limitations caused by variations in sunlight availability, enabling the generation of electricity even during non-optimal conditions. These diverse CSP technologies contribute to the expansion of clean energy infrastructure, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating environmental impact.
As the renewable energy sector continues to evolve, the advancements in CSP technology offer promising opportunities for sustainable energy generation on a large scale.
See How Solar Panels Produce Power

Installing Home Solar
Solar power can significantly benefit homeowners and business owners alike. Installing solar panels on your house or other building can help reduce electricity costs and generate backup energy during power outages or severe weather. If you’ve been thinking about going solar, there’s much to consider.
Solar energy costs vary depending on several factors, including soft costs like loans and financing, permitting, and installation. You can learn more about how much solar panels cost here.
Ready to Go Solar?
If you’re ready to switch to renewable solar energy, Axia is here to make it possible. We guide you through the entire transition, ensuring you feel informed and empowered through every step of our simple and seamless process.
Get in touch with one of our solar advisors today to discuss solar panel costs, get a custom quote, or begin your solar power installation. We can’t wait to help electrify your life!
Learn More
Want to learn more about how solar works? Check out these related articles. Have a question you can’t find an answer to? Contact us or chat live with an expert today.
Related Articles

- https://www.energy.gov/eere/solar/solar-photovoltaic-technology-basics ↩︎
